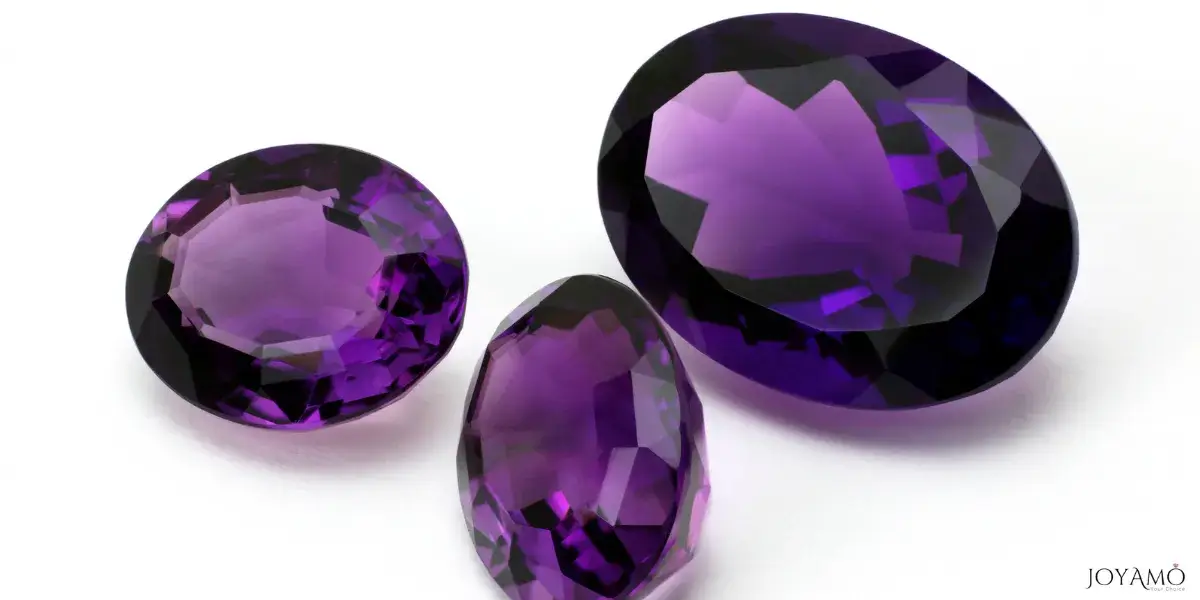
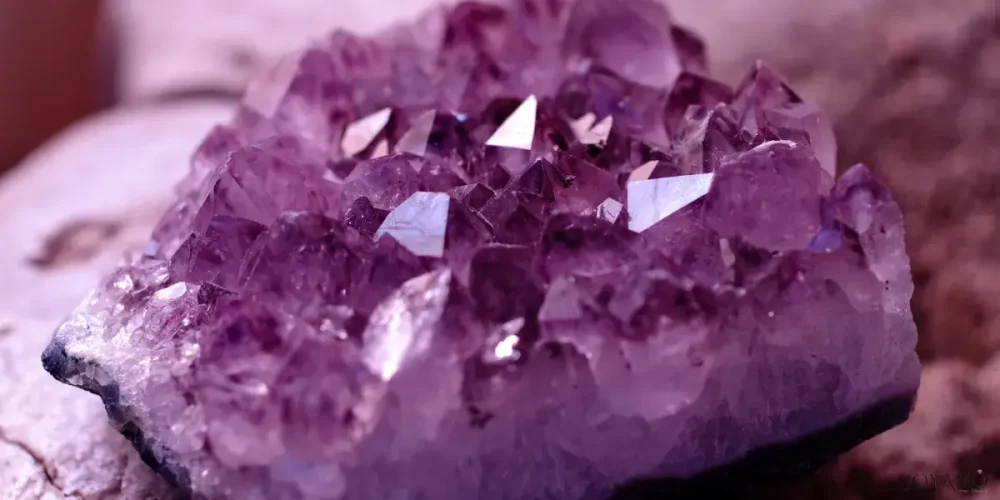
Amethyst, February’s adored birthstone, captivates with its incredible purple hue and magic allure.
Believed to possess both physical and spiritual properties, this gemstone has long been revered for its beauty and purported healing energies.
Named after the Greek word “amethystos,” meaning “not intoxicated,” ancient Greeks believed amethyst could protect against drunkenness, a belief reinforced by the wine-like color of the stone.
It was often worn as an amulet to ward off intoxication and promote clarity of mind.
Beyond its folklore, amethyst is loved for its stunning color range, from delicate lilacs to deep purples, and its exceptional clarity.
As a variety of quartz, it forms within geodes in volcanic rock, and its color is typically the result of iron impurities within the crystal lattice.
In addition to its aesthetic appeal, amethyst is associated with numerous metaphysical properties.
It is said to promote emotional balance, spiritual growth, and clarity of thought, making it a popular choice for meditation and healing practices.
In astrology, amethyst is also recognized as the birthstone for Aquarius, the zodiac sign that spans from January 20th to February 18th.
For Aquarians, amethyst is thought to amplify their natural intuition and bring clarity to their innovative ideas.
This association further enhances the stone’s significance, intertwining its mystical properties with the unique characteristics of those born under the sign of the Water Bearer.
As such, amethyst serves not only as a symbol of February birthdays but also as a celestial talisman for those who identify with the qualities of Aquarius, fostering their connection to the cosmos and their inner selves.
Worn as jewelry or kept as a precious stone, February’s birthstone, amethyst, continues to fascinate and inspire with its timeless beauty and rich symbolism.
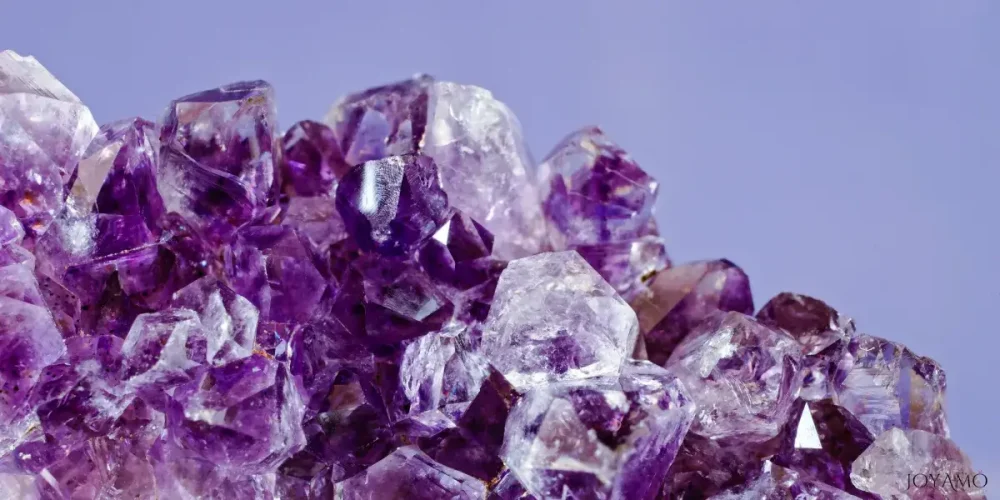


1) History and origins of amethyst
Throughout history, amethyst has a story that dates back thousands of years blending myths, legends, and geological discoveries.
As part of the quartz family, amethyst gets its name from the word “amethystos,” meaning “not intoxicated.”
This name originates from a belief suggesting that using vessels or items made of amethyst could prevent intoxication.
At times, amethyst was highly regarded in cultures.
The Ancient Egyptians valued it for its symbolism and protective qualities against spirits.
In mythology, the roots of amethyst are intertwined with a story of change.
Legend has it that a maiden named Amethysta was transformed into a quartz crystal by the goddess Diana to shield her from Bacchus advances, the god of wine.
Bacchus then poured wine over the stone out of regret, turning it purple and establishing the connection between amethyst and sobriety.
In history, the ancient Romans greatly appreciated amethyst and used it to create jewelry and talismans.
It embellished the crowns, rings, and staffs of rulers and religious figures as a symbol of authority, protection, and devotion.
Geologically, amethyst develops within cavities in rocks where fluids rich in silica gradually deposit crystals over thousands of years.
Amethyst gets its hue from iron impurities in the crystal structure displaying shades of soft lilac to rich violet.
In the Middle Ages, amethyst retained its value as a representation of spirituality and enlightenment.
It was believed to possess healing properties guarding against toxins and enhancing clarity.
The Renaissance era witnessed a renewed interest in amethyst among royalty and clergy.
It adorned crowns, religious attire, and exquisite jewelry symbolizing wisdom, modesty, and spiritual growth.
Nowadays, amethyst continues to be a treasured gemstone used in jewelry and decorative items. It is not only loved as the birthstone for February but also revered as a charm for inner peace, intuition, and personal transformation.
From legends to present-day charm, the captivating history and origins of amethyst tell a story of cultural importance and geological wonder ensuring its timeless allure for future generations.
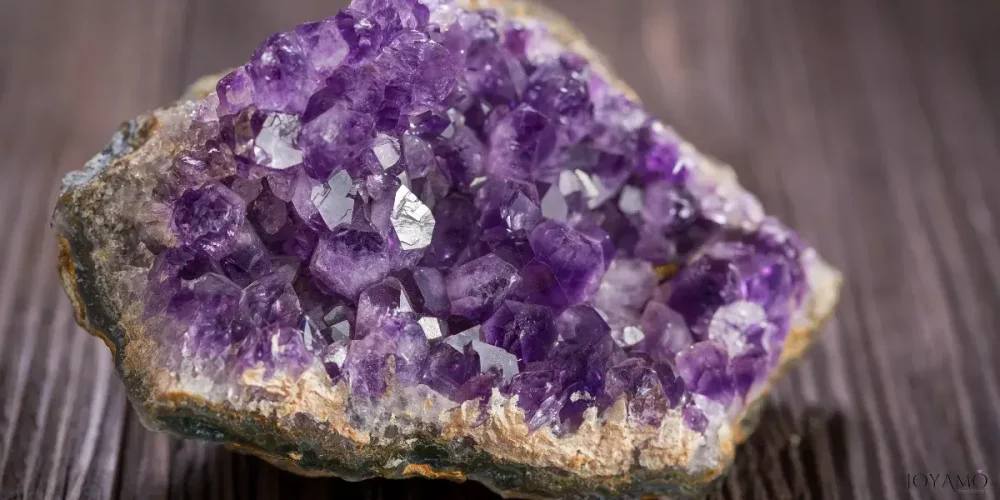

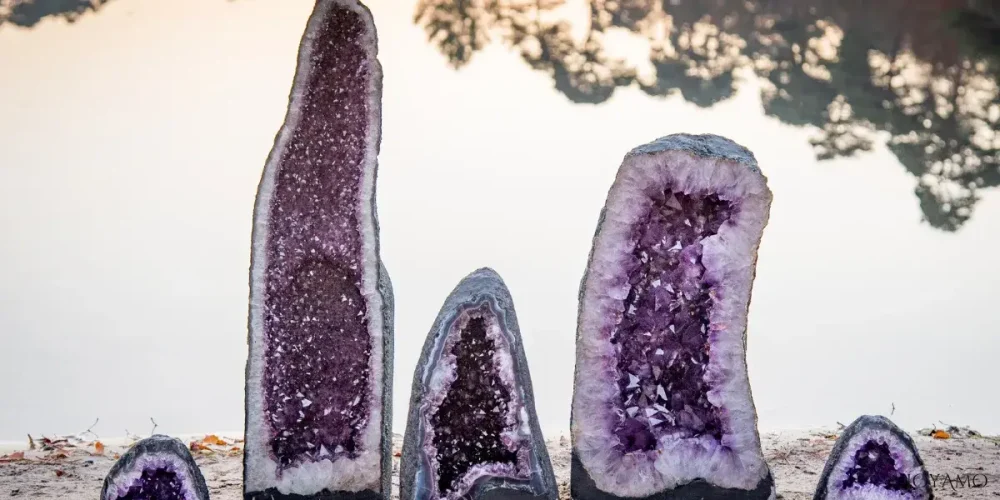
2) Amethyst geological formation and major mining locations
Amethyst, a type of quartz, is renowned for its beautiful purple shades and is formed through a mix of volcanic activity and hydrothermal processes.
It typically develops in cavities like geodes found in rocks such as granite or basalt.
These geodes are created when gas bubbles get trapped within rock during eruptions.
As the magma cools and solidifies over time, the trapped gas forms hollow spaces where minerals can grow.
The creation of amethyst involves the deposition of silica fluids with amounts of iron inside these geodes.
When these fluids seep into the cavities and cool down they crystallize, leading to the formation of quartz crystals.
The presence of iron impurities in the crystal structure gives amethyst its hue ranging from light lavender to deep violet.
Amethyst is mined in locations with significant deposits found in different countries.
Brazil stands out as a producer of amethyst in Rio Grande do Suls southern state.
The city of Ametista do Sul (translated as “Amethyst of the South”) is famous for its high-quality amethyst reserves.
Zambia is another source of amethyst, with substantial deposits discovered in the southern part of the country.
Zambian amethyst is highly valued for its color and clear appearance.
Uruguay is known for its amethyst geodes, particularly from the Artigas region in the country’s northwestern part.
These geodes often contain purple crystals that are sought after by collectors and jewelry makers alike.
Other known places where amethyst is mined include Madagascar, Russia, India, and the United States.
Each location offers variations in color, clarity, and crystal structure, adding to the charm and diversity of this captivating gemstone.
The natural formation of amethyst and its various mining sites highlight its reputation as a gem appreciated for both its beauty and spiritual significance.
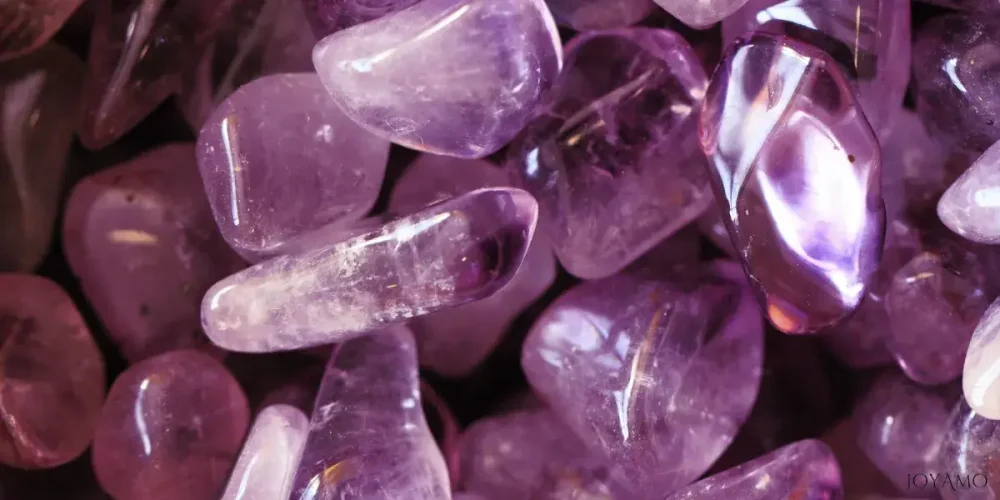


3) Physical properties of amethyst
Amethyst, a captivating gem cherished for its beauty and spiritual significance, possesses a range of physical traits that enhance its charm and desirability.
Its rich hue and intricate crystal structure make amethyst a source of fascination for both gem enthusiasts and researchers.
Fundamentally, amethyst belongs to the quartz family, a prevalent mineral found abundantly on our planet.
It shares the chemical makeup as quartz varieties primarily composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2).
What distinguishes amethyst is its coloration, which arises from minute traces of iron impurities nestled within its crystal lattice.
The color spectrum of amethyst is diverse, spanning from lilacs to violet tones.
The richness and depth of color can vary based on factors like the concentration of iron impurities and the presence of elements.
Certain amethyst samples showcase zoning effects where colors are unevenly distributed throughout the crystal structure resulting in patterns and variations.
Clarity stands out as another feature in assessing amethyst’s characteristics.
Superior specimens are highly valued for their transparency and absence of imperfections that might diminish their beauty.
Inclusions such as mineral crystals or gas bubbles trapped during formation can impact the clarity and overall aesthetics of amethyst.
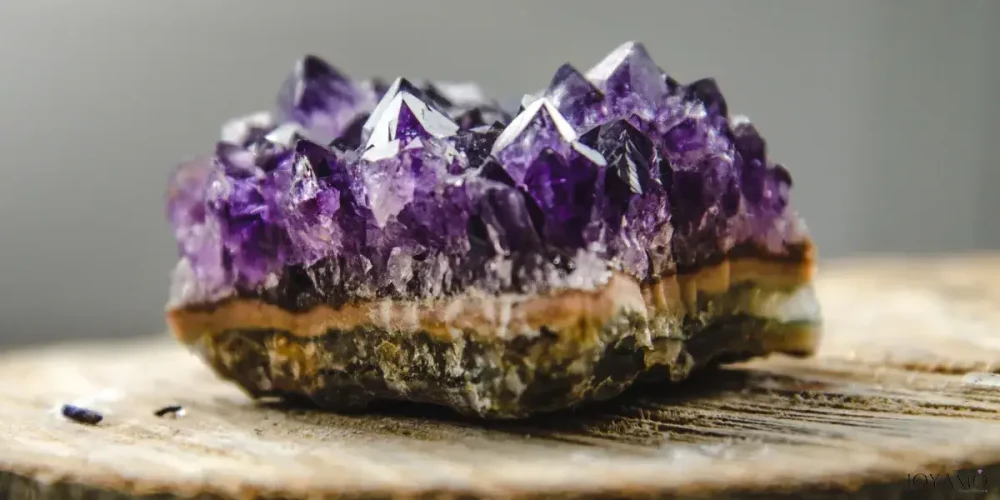
Amethyst crystals typically grow in prism shapes with six endings called hexagonal prisms.
These crystals range in size from clusters to geodes containing tall crystals reaching several feet high.
The formation of amethyst crystals is influenced by factors such as temperature, pressure, and the presence of minerals.
On the scale, amethyst has a hardness of 7 making it quite durable and suitable for jewelry making.
However, like all gemstones amethyst can get chipped if handled roughly or exposed to materials.
Amethyst shows pleochroism, which means it can exhibit colors depending on the viewing angle.
Although the pleochroism in amethyst is usually subtle compared to other gemstones, it can still impact the stone’s appearance in larger pieces.
One fascinating characteristic of amethyst is its ability to change color when exposed to heat or radiation.
This process known as irradiation can modify the stone’s color resulting in hues like orange or green.
Treated amethyst varieties may look visually appealing but are often less valuable than untreated specimens.
- Chemical Composition: Silicon Dioxide (SiO2)
- Color: Ranges from delicate lilacs to deep violets
- Transparency: Transparent to translucent
- Crystal Structure: Hexagonal prisms with six-sided terminations
- Hardness (Mohs Scale): 7 (relatively durable)
- Clarity: High-quality specimens are transparent with minimal inclusions
- Pleochroism: Exhibits subtle color changes when viewed from different angles
- Size: Can range from small druzy clusters to large geodes
In addition to its aesthetic appeal, amethyst is renowned for its metaphysical properties and purported healing energies
It is believed to promote emotional balance, spiritual growth, and mental clarity, making it a popular choice for meditation and holistic therapies.
In general, the unique physical characteristics of amethyst play a role in its reputation as a cherished gemstone globally.
From its color to its crystal formation amethyst remains enchanting and motivational with its enduring charm and mystical appeal.
Key physical properties of amethyst
| Physical Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Silicon Dioxide (SiO2) |
| Color | Ranges from delicate lilacs to deep violets |
| Transparency | Transparent to translucent |
| Crystal Structure | Hexagonal prisms with six-sided terminations |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 7 (relatively durable) |
| Clarity | High-quality specimens are transparent with minimal inclusions |
| Pleochroism | Exhibits subtle color changes when viewed from different angles |
| Size | Can range from small druzy clusters to large geodes |
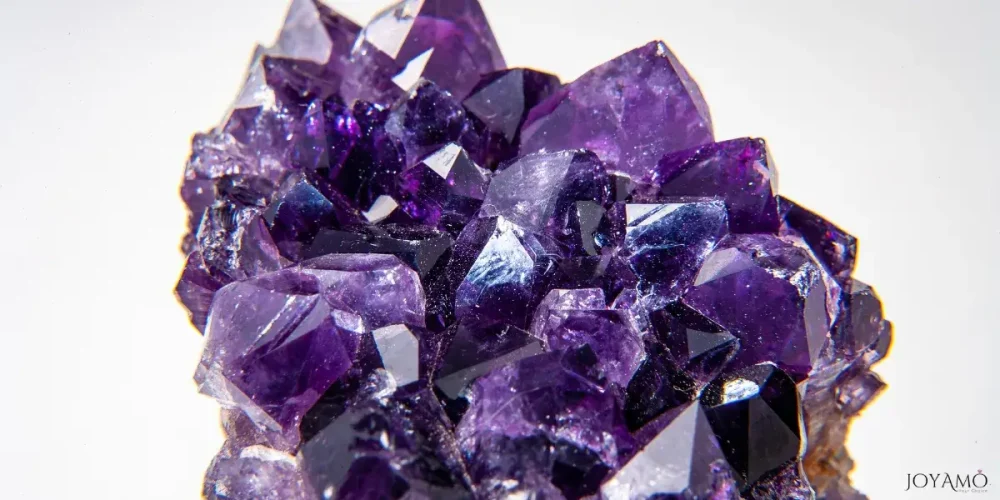
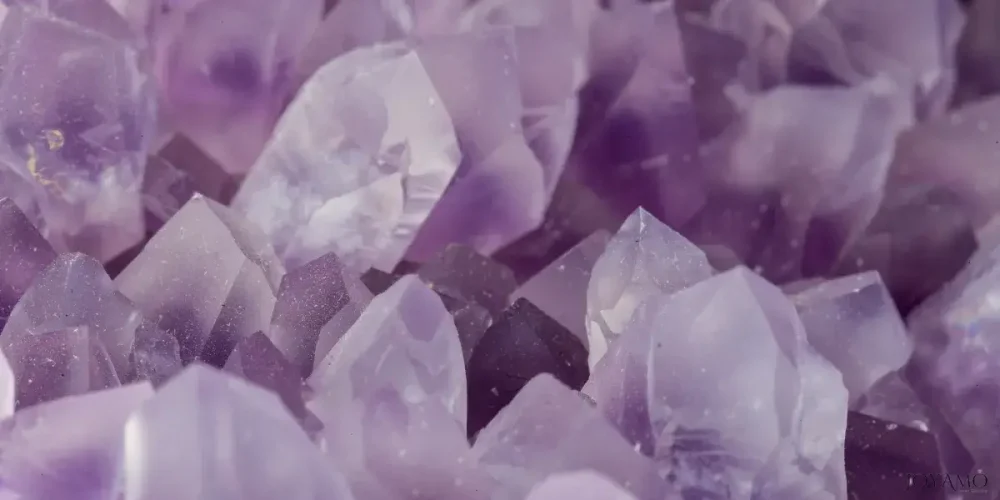


4) Symbolism and Meanings Associated with Amethyst
Amethyst, known for its enchanting shades, has been rich in meanings and interpretations across different cultures and traditions over the years.
Sobriety and Clarity: In myths, amethyst was believed to prevent intoxication leading to its name “amethystos,” which translates to “not drunk.” This link to clarity of mind and sobriety has remained relevant through time.
Spirituality and Enlightenment: Amethyst has a connection with development and enlightenment. Its purple hue is thought to activate the eye chakra encouraging intuition and inner wisdom.
Protection and Healing: Throughout history amethyst has been seen as a gemstone that shields against energies and psychic assaults. It is commonly utilized in rituals to form a shield of light, around individuals.
Royalty and Power: In the past, amethyst was regarded as a gemstone symbolizing royalty and nobility. It adorned the regalia of monarchs like crowns, scepters, and jewelry as a representation of power, authority, and divine linkage.
Romance and Devotion: Amethyst also carries connotations of love and devotion. Amethyst is commonly given as a symbol of love and commitment often seen in engagement rings to represent loyalty and devotion.
In general, amethyst carries meanings, from clarity and sobriety to spirituality and safeguarding making it a valued gemstone rich in significance.
5) Metaphysical and Healing Properties of Amethyst
Apart from its appeal amethyst is esteemed for its properties believed to enhance emotional stability, spiritual development, and overall well-being.
Emotional Stability: Amethyst is known to ease stress, anxiety, and fear. Its subtle energy promotes peace, serenity, and inner balance.
Spiritual Development: Often used in meditation and spiritual rituals to boost intuition and deepen connections. It is thought to activate the eye chakra expanding the mind towards consciousness.
Protection: Considered a crystal that shields against negative energies and psychic disturbances. It envelops the aura with a shield of energy, by converting negativity into positive vibrations.
Physical Healing: In healing practices, amethyst is thought to enhance well-being and promote good health. It is believed to ease headaches improve sleep quality and boost vitality.
Energizing: Amethyst is renowned for its cleansing abilities removing energies and obstacles. It is commonly used to purify crystals helping them regain their equilibrium and harmony.
Overall amethyst is highly valued for its healing properties providing assistance and insight on the path to holistic well-being and spiritual growth.
6) Notable Amethyst gemstones and Jewelry Pieces
Notable amethyst gemstones and jewelry pieces have graced royalty collections, adorned monarch crowns, and captivated the hearts of gem enthusiasts throughout history.
From magnificent specimens to exquisite jewelry creations, amethyst continues to inspire awe and admiration with its timeless beauty and mystical allure.
One notable amethyst gemstone is the “Delhi Purple Sapphire,” a legendary 135.8-carat amethyst that was once part of the Russian crown jewels.
Believed to have originated from India, this remarkable gemstone boasts a deep purple hue and exceptional clarity, making it one of the largest and most valuable amethysts in the world.
Another renowned amethyst is the “Brazilian Princess Amethyst,” a spectacular 45.5-carat gemstone that showcases the rich color and brilliance of Brazilian amethysts.
This exceptional gemstone, with its regal purple hue and exquisite faceting, exemplifies the unparalleled beauty of amethyst from the mines of Brazil.
In addition to these notable gemstones, amethyst has also been featured in exquisite jewelry pieces that showcase its beauty and versatility.
From delicate earrings to statement necklaces, amethyst lends its distinctive color and charm to a wide range of jewelry designs.
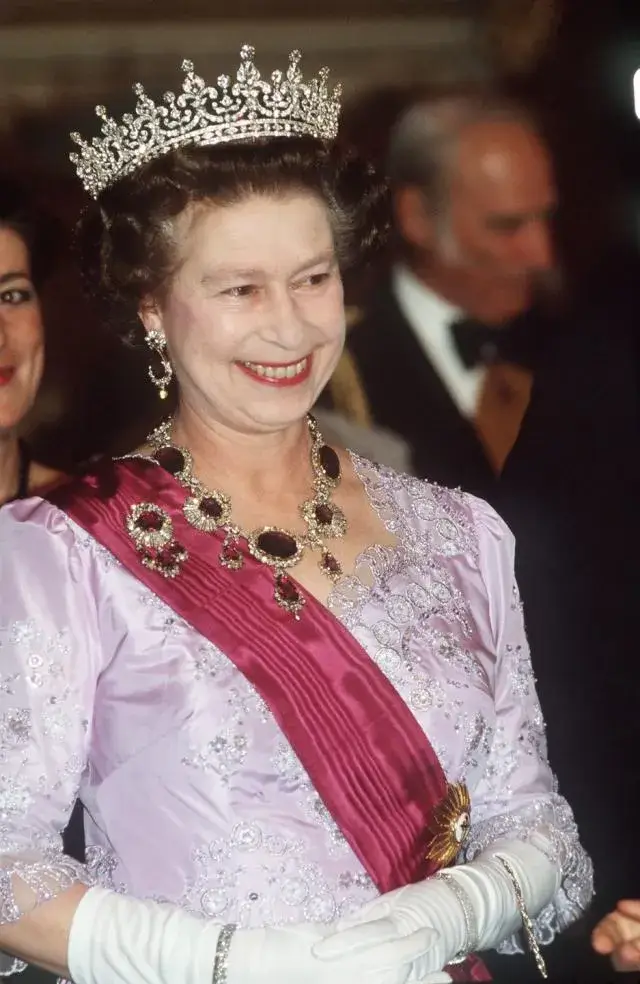
One notable example is the “Amethyst and Diamond Pendant Necklace” worn by Queen Elizabeth II, featuring a stunning amethyst pendant surrounded by sparkling diamonds.
This elegant piece, crafted by renowned jewelry house Garrard, exemplifies the timeless appeal of amethyst in royal jewelry.
Overall, notable amethyst gemstones and jewelry pieces exemplify this beloved gemstone’s enduring allure and significance.
Adorning crowns or embellishing everyday jewelry, amethyst continues to captivate with its radiant beauty and mystical charm.



 SHIPPING
SHIPPING





